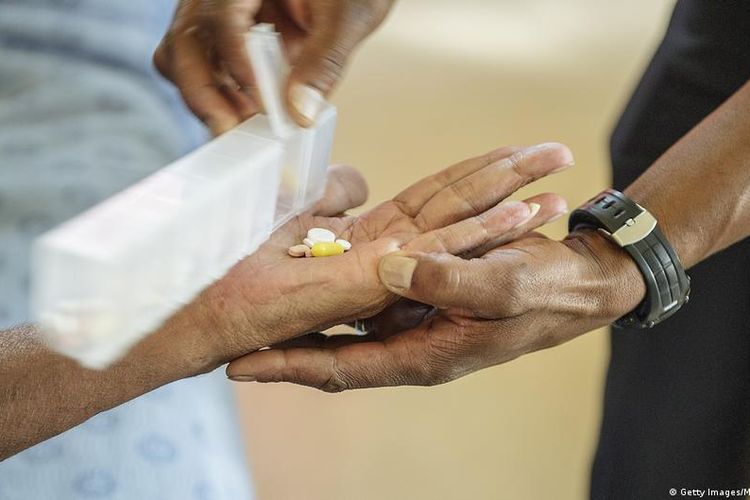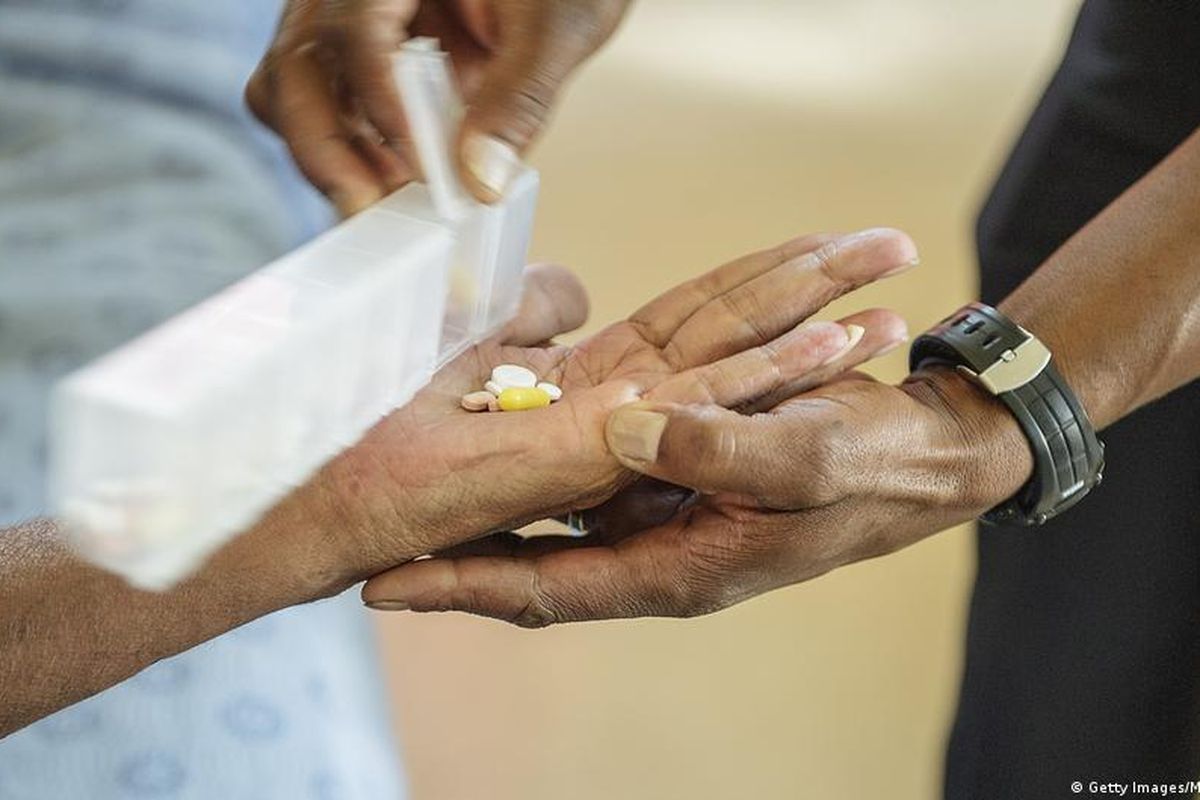
KOMPAS.com - In 2010, Phumeza Tisile, then a first-year student at Cape Town University in South Africa, noticed that she couldn't climb the stairs easily like other students. She would become tired quickly and had lost a lot of weight.
"That's when I saw that there was something wrong," Tisile told DW. "But I never thought that it might be TB."
After other diseases were ruled out, a chest X-ray revealed that Tisile did have tuberculosis (TB), and her journey to recovery — a feat that would take three years and eight months — began.
Also read: Asian Frontline Medics in US Face Hate Amid Covid-19
Despite being a preventable and curable disease, TB killed 1.4 million people in 2019, according to the World Health Organization (WHO), making it the world's most infectious disease killer, ahead of both HIV and malaria.
About half of all people with TB can be found in eight countries in the Global South, but TB cases still occur in most countries.
On March 4, 2021, the German city of Krefeld announced that a 17-year-old student had died from TB.
In 2019, there were 4,791 cases of TB in Germany and 129 people died from the disease, according to the Robert Koch Institute, a Germany government agency responsible for disease control and prevention.
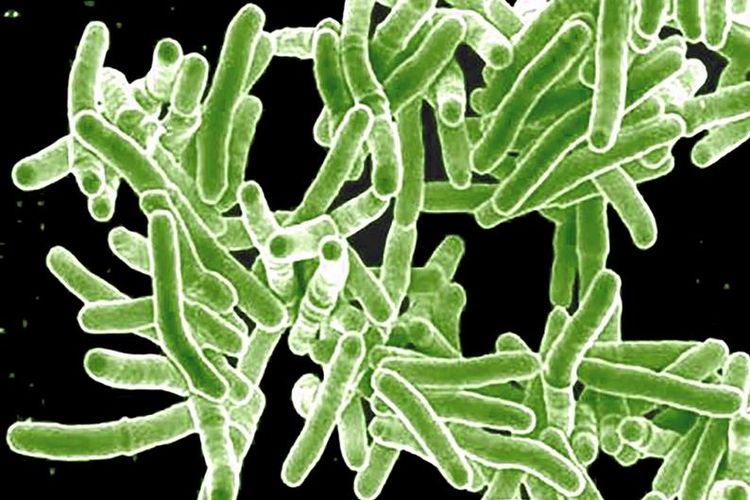 Mycobacterium tuberculosis is the bacteria that causes tuberculosis
Mycobacterium tuberculosis is the bacteria that causes tuberculosisWhat is TB?
TB is caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis and usually affects the lungs, but it can be located in other parts of the body, too. It is spread through the air when people with active TB in their lungs cough, sneeze or spit.
It is not spread by sharing eating utensils, shaking hands, hugging, touching bed linen or toilet seats, sex, or sharing saliva when kissing someone. Symptoms include a cough, chest pain, fatigue, fever and weight loss.
Also read: Indonesia to Ban New Year's Celebration in Public Places
Close or long-term contact is usually required for someone to become infected. About one-quarter of the world’s population is estimated to be infected with TB bacteria, according to the WHO, and only 5% to 15% of these people develop active TB disease.
Most people who have had treatment for a few weeks are no longer contagious.
Overcrowded homes and spaces, malnutrition, HIV, substance abuse and diabetes are some of the risk factors for TB. People can also have a latent TB infection that might become active even years later when their immune system is weak.
COVID-19 erases years of TB progress
Though scientists have worked around the clock to develop vaccines for Sars-CoV-2, there is only one effective vaccine for TB, Bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG). It was first tested on humans in 1921. The BCG vaccine is quite effective in children but doesn't work very well for adults.
Scientists recently developed another vaccine based on BCG. Once the vaccine has successfully completed clinical testing, there are plans to use it against tuberculosis worldwide within the next few years.