What Can Be Done about Electric Vehicle Battery Recycling in Indonesia

JAKARTA, KOMPAS.com – Indonesia, the world’s biggest nickel producer, began to develop its first electric vehicle (EV) battery plant last year. With the material’s use in lithium-ion batteries for EVs constantly on the rise, the nickel industry is gearing up for growth, with a flurry of activity as producers look to get their hands on this now-essential battery metal.
Nickel will accomplish all this at a lower cost. It is a major benefit as battery cost has also been a significant deterrent to market acceptance for the country’s current capital, Jakarta.
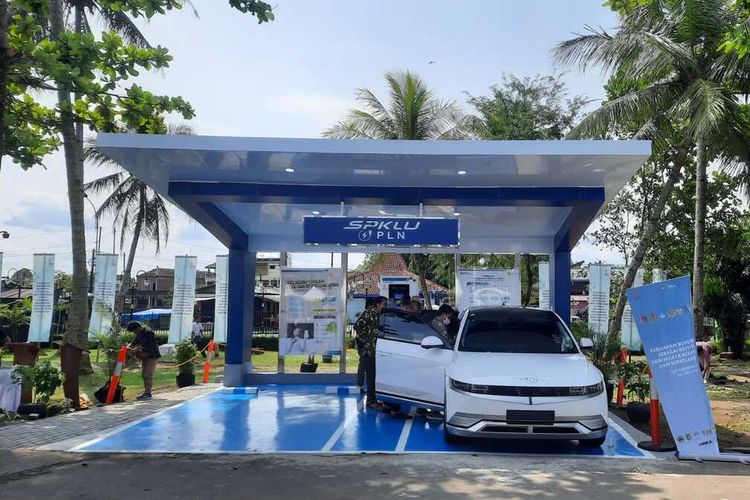
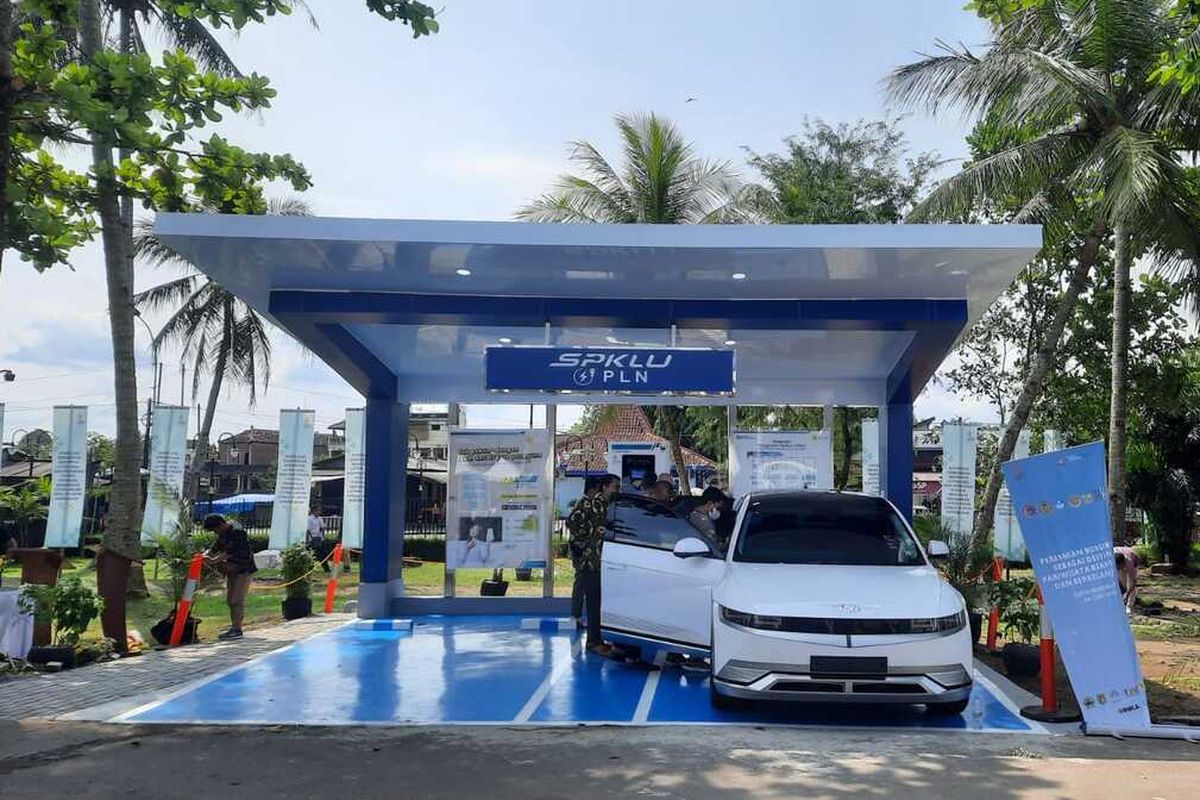
Indonesia’s President Joko Widodo issued Presidential Regulation No. 55/2019 on the acceleration of battery electric vehicle programs for road transportation (PR 55/2019) on Aug. 8, 2019. This regulation includes measures to promote and accelerate the implementation of battery electric vehicle programs. Besides, using solar panels to charge EVs is a great way to save costs and get on the path to a better future.
Also read: Indonesia Ready to Become Major Player in Electric Vehicle Industry: Minister
A BBC news report said that “in 10 to 15 years when there are large numbers coming cars to the end of their life, it’s going to be very important that we have a recycling industry.”
“While most EV components are much the same as those of conventional cars, the big difference is the battery. While traditional lead-acid batteries are widely recycled, the same can’t be said for the lithium-ion versions used in electric cars,” it added.
Foreign partnerships
In an effort to accelerate the implementation of battery electric vehicle programs, the government can build partnerships with other countries, such as Australia.
A report stated that Indonesia is Australia’s biggest market and a major source of nickel, the main component of lithium-ion batteries for EVs. The cooperation in this area could become the largest bilateral agreement between the two countries.
Australia has an act relating to the protection of the environment and the conservation of biodiversity called the EPBC Act. Under the Act, the Department of Agriculture, Water and the Environment (DAWE) is responsible for managing the environmental assessment and approval process, its official website stated.
Also read: Indonesia, South Korea’s LG Group Sign Electric Vehicle Battery MOU Worth $9.8 Billion
Lithium batteries have a long-lasting impact if the waste is disposed of irresponsibly. This type of battery contains various metals such as cobalt (Co), copper (Cu), nickel (Ni), and lead (Pb) which are at risk of contaminating the environment around the disposal site.
The batteries are also known to be prone to catching fire and exploding. They have the potential to cause problems if ended in landfills.
In Australia, the key environmental legislation requires regulators in each state and territory to maintain public registers containing relevant environmental information. The regulators generally keep public registers relating to, among others, environmental licenses and permits, enforcement actions, contaminated land, and water entitlements.
In Indonesia, however, Government Regulation No.22/2021 on environmental protection and management has revoked several related government regulations, including Government Regulation No.27/2012 on the environmental permit and Government Regulation No.101/2014 on the management of hazardous and toxic waste or locally known as B3.